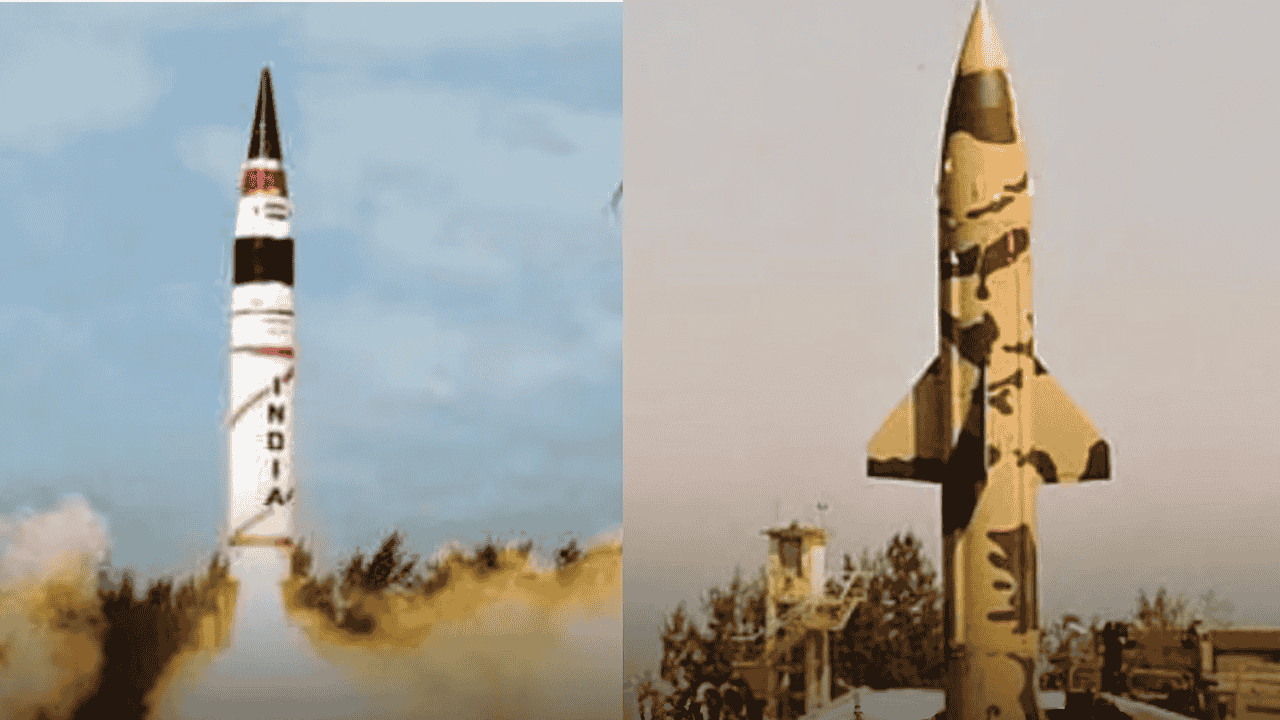
India has taken another significant step in strengthening its defense capabilities. On 17th July 2025, India successfully test-fired two key ballistic missiles—Prithvi-2 and Agni-1—from the Integrated Test Range (ITR) in Chandipur, Odisha. The test was conducted under the supervision of the Strategic Forces Command to validate all operational and technical parameters.
Key Highlights of the Missile Test
Prithvi-2 Missile Test
Prithvi-2 is the first missile developed under India’s Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP). The test was conducted from Launch Pad-III. Key features of Prithvi-2 include:
Range: Up to 350 kilometers
Payload Capacity: Up to 500 kilograms
Propulsion System: Liquid-fueled
Warhead: Capable of carrying both conventional and nuclear warheads
Agni-1 Missile Test
The Agni-1 missile was tested from Abdul Kalam Island. It is a vital part of India’s strategic missile arsenal. Key specifications of Agni-1:
Range: Between 700–900 kilometers
Payload Capacity: 1,000 kilograms
Propulsion System: Single-stage, solid-fuel
Weight: 12 tons
Length: 15 meters
Role of Strategic Forces Command (SFC)
The Strategic Forces Command (SFC) is a part of India’s Nuclear Command Authority (NCA) and is responsible for managing the country's strategic nuclear arsenal. It was established on January 4, 2003. Key responsibilities include:
Nuclear Weapon Management: Command and control of all strategic forces
Implementation of NCA Orders: Executes the directives of the Nuclear Command Authority
Routine Testing: Ensures operational readiness of missile systems
Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur
The ITR in Chandipur is a premier missile testing facility under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). It offers:
Missile Testing Capabilities: Suitable for multiple missile variants
Two Test Complexes: Launch Complex-III (LC-III) in Chandipur and Launch Complex-IV (LC-IV) on Abdul Kalam Island
Safe Testing Environment: Located along the coastline for secure trials
Significance of IGMDP
The Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) was launched in 1983 under the leadership of Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam. It aimed to develop five missile systems:
Prithvi: Short-range surface-to-surface missile
Agni: Medium to long-range surface-to-surface missile
Akash: Medium-range surface-to-air missile
Trishul: Short-range surface-to-air missile
Nag: Anti-tank guided missile
Post-Operation Sindoor Significance
This missile test comes two months after Operation Sindoor, where India demonstrated the supremacy of its air defense systems. The missiles tested at Chandipur’s ITR played a notable role during that operation.
Technical Analysis
Prithvi-2 Technical Features
Accuracy: CEP (Circular Error Probable) of 100–300 meters
Launch Preparation Time: 2–3 hours
Mobility: Can be launched from road-mobile launchers
Warhead Types: Compatible with five different warhead configurations
Agni-1 Technical Features
Propulsion: Single-stage solid fuel
Diameter: 1 meter
Speed: 2.5 km/second
Operational Since: Inducted into Indian Army in 2007
Defence Minister’s Statement
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh congratulated the Indian Army, DRDO, and defence industry on the successful test, calling it a “remarkable achievement.”
Parallel Test of Akash Prime
A day before the above tests, on 16th July, the Akash Prime missile was successfully tested in Ladakh. This test was significant for the following reasons:
High Altitude: Conducted at an altitude above 4,500 meters
Near LAC: Carried out close to the Line of Actual Control
Indigenous RF Seeker: Used a fully indigenous radio frequency seeker
India’s Missile Policy
India’s missile policy is based on the doctrine of Minimum Credible Deterrence (MCD). Key features:
No First Use (NFU): India will not initiate nuclear attack
Dual Capability: Can carry both conventional and nuclear payloads
Quick Response: Capable of swift retaliatory strikes
India’s Global Position in Missile Power
Currently, only the US, China, and Russia possess advanced missile systems. India is catching up rapidly with:
Indigenous Development: Entirely Indian-made systems
Production Capacity: Capable of producing 40 missiles annually
Variety: Wide range of missiles with varying ranges and capabilities
Economic Angle of Missile Development
India’s defence exports reached ₹21,083 crore in FY 2023-24 and set a target of ₹35,000 crore by 2025:
Aatmanirbhar Bharat: Emphasis on indigenous defence production
Export Potential: Indian-made missiles suitable for international buyers
Technological Independence: Reduces reliance on foreign equipment
Future Plans
India aims to further improve its strategic missile capabilities through:
Agni-6: ICBM with a range of 8,000–10,000 kilometers
Hypersonic Missiles: Like ET-LDHCM under development
MIRV Technology: Multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicles
Why This Matters for Your Exam Preparation
Defence Studies
This news is critically relevant for UPSC and other competitive exams in the field of defence and strategic studies. The test of Prithvi-2 and Agni-1 highlights India's offensive and deterrent capabilities.
Science & Technology
Knowledge of missile technology, propulsion systems, and navigation is highly relevant to the Science & Technology section. The IGMDP programme and its outcomes often appear in exams.
Current Affairs
This test on 17 July 2025 is among the latest developments and is likely to be asked in both Prelims and Mains. The role of the Strategic Forces Command and DRDO is crucial context.
Internal Security
India’s missile doctrine, Nuclear Command Authority, and preparedness are important for questions in GS Paper 3 under internal security. Operation Sindoor provides additional context.
International Relations
India’s growing missile capability and its strategic balance affect its regional and global influence, making this relevant for international affairs questions.
🔑 Key Facts to Remember:
Test Date: 17 July 2025
Test Location: Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur
Prithvi-2 Range: 350 km | Payload: 500 kg
Agni-1 Range: 700–900 km | Payload: 1,000 kg
Supervision: Conducted by Strategic Forces Command
IGMDP Launched: 1983 under Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam
SFC Established: 4 January 2003
For similar UPSC-focused current affairs updates, visit:
👉 Atharva Examwise - Defence & Strategy Updates